Introduction to Structural Steel Construction
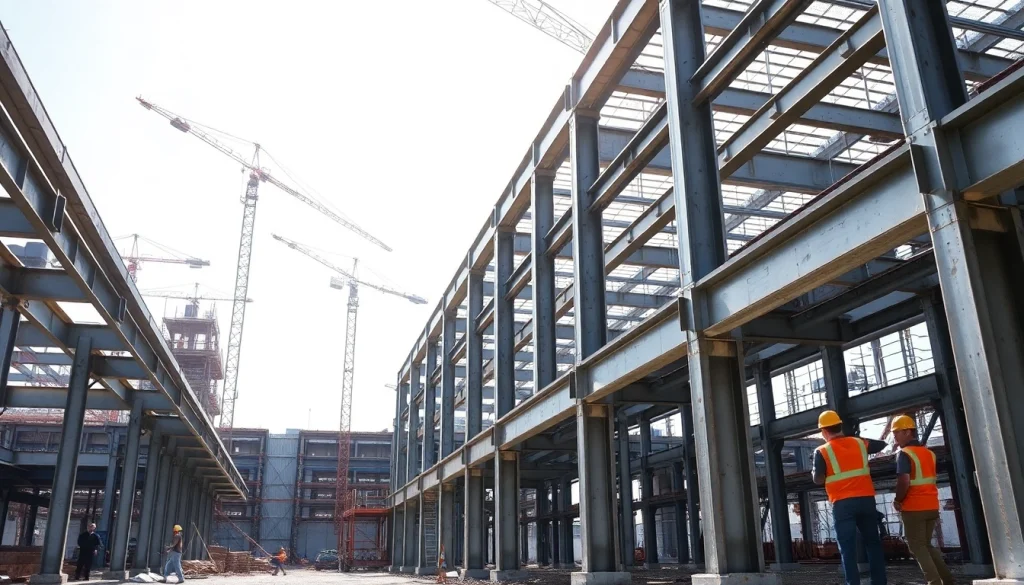
Structural steel construction is a critical component of modern architecture and engineering, recognized for its strength and versatility. Defined as the use of steel shapes and elements designed to support loads and withstand environmental forces, structural steel has become a preferred material in various building projects worldwide. The significance of structural steel construction extends beyond mere utility; it serves as the backbone of skyscrapers, bridges, and a myriad of other structures that define our urban landscapes.
What is Structural Steel?
At its core, structural steel is made from carbon steel and is designed to perform efficiently under various loads. It is produced in various shapes (such as beams, columns, and plates) and is characterized by its high strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and adaptability. Structural steel can be categorized into two primary types: rolled sections and fabricated sections, allowing for a wide range of applications in construction.
History and Evolution of Structural Steel
The evolution of structural steel construction can be traced back to the early 19th century when its properties were harnessed to create more substantial and taller structures. The Industrial Revolution sparked the need for stronger materials, leading to innovations in steel production like the Bessemer process, which made steel more affordable and accessible. Over the decades, iconic buildings like the Eiffel Tower and the Chrysler Building showcased the advancements in structural steel, setting standards for design and efficacy.
Importance in Modern Engineering
In modern engineering, structural steel is pivotal in meeting the demands of contemporary construction. Its properties allow for a high degree of design freedom, which is especially important in urban design, where space is limited and aesthetics play a significant role. Furthermore, structural steel’s fire resistance, seismic performance, and sustainability (especially with the recycling of steel) make it indispensable in various civil engineering projects.
Types and Grades of Structural Steel
Common Types of Structural Steel
Structural steel comes in diverse shapes and sizes, each designed for specific applications. Common types include:
- I-Beams: Used primarily for beams and frames.
- H-Beams: Known for their high load-bearing capacity.
- C-Channels: Often used for supports and frames.
- Angle Iron: Versatile utility in various frameworks.
- Plate Steel: Used for structural applications, including bridges and buildings.
Understanding Steel Grades
Steel grades are essential for determining the appropriate application of structural steel. Each grade indicates the yield strength and ductility of the steel. Common grades include:
- ASTM A36: A low carbon structural steel used for general purposes.
- ASTM A992: Often utilized in steel building frames due to its superior strength.
- ASTM A572: Known for its high strength and good weldability, suitable for various structures.
Choosing the Right Type for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate type and grade of structural steel depends on several factors, including load requirements, environmental conditions, and aesthetic needs. Consulting with structural engineers and architects during the planning phase is crucial to ensure the selected materials align with the overarching design and functionality goals.
Design and Fabrication Processes
Structural Steel Design Considerations
When designing with structural steel, numerous considerations come into play, including load calculations, environmental factors, and compliance with local building codes. Engineers utilize advanced modeling software to analyze stress points and load distributions, ensuring safety and performance.
Fabrication Techniques and Technologies
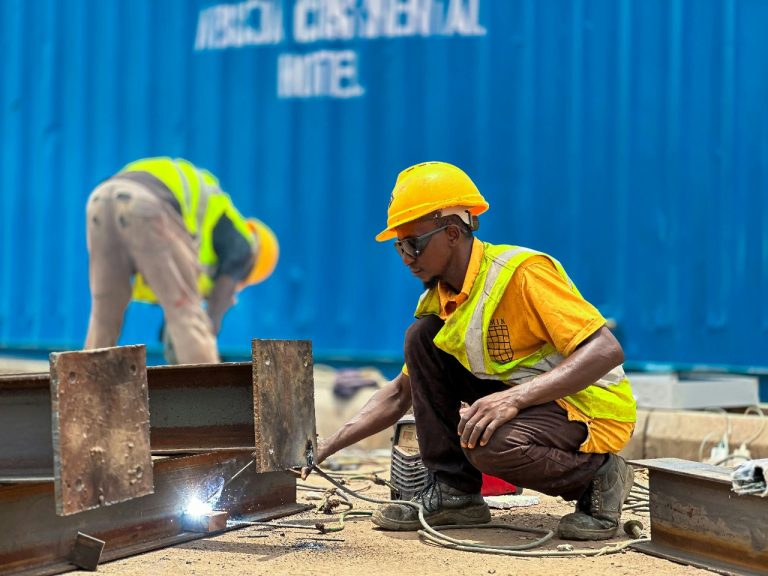
The fabrication of structural steel involves a series of processes, including cutting, bending, and welding metal pieces into the desired shape. Modern techniques often incorporate CNC machinery for precision, allowing for faster and more cost-effective production. Automation is also increasingly employed in steel fabrication, which enhances productivity and reduces human error.
Best Practices for Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is paramount in structural steel fabrication. Adopting practices such as regular inspections, adhering to industry standards (like the AISC certification), and implementing process documentation are vital. Engaging certified inspectors to examine welds and connections ensures that the finished product meets both safety and durability expectations.
Construction Methods and Techniques
Popular Methods in Structural Steel Construction
When it comes to erecting structural steel, several methods are commonly employed:
- Bolted Construction: Simple and efficient for on-site assembly.
- Welded Construction: Offers stronger joints which are ideal for heavy-duty applications.
- Prefabricated Elements: Allows for quicker assembly and reduced workload on-site.
On-Site Assembly and Erection
The on-site assembly of structural steel involves the meticulous arrangement and bolting or welding of steel components into a coherent structure. Heavy machinery, such as cranes, is typically used to lift and position the steel elements. Proper planning and staging are essential to minimize delays and enhance worker safety during the erection process.
Safety Protocols and Worker Training
Worker safety is a top priority in any construction project, especially in structural steel construction. Implementing robust safety protocols, such as regular training sessions, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and adherence to OSHA regulations, is vital to mitigating risks and ensuring a safe working environment. Safety drills and the establishment of clear communication channels between team members are also crucial to preventing accidents on-site.
Future Trends in Structural Steel Construction
Sustainable Practices in Steel Construction
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in construction, structural steel’s recyclability and durability offer significant advantages. Initiatives such as using recycled steel, employing energy-efficient fabrication methods, and designing for disassembly are gaining traction within the industry. These practices not only reduce the environmental footprint but can also lower long-term operational costs.
Innovations Shaping the Future
Technological advancements are revolutionizing structural steel construction. Innovations such as 3D printing of steel components, robotics for assembly, and advancements in steel alloys are enhancing efficiency, reducing waste, and improving overall structural performance. Emerging digital tools involving AI and machine learning facilitate better project management and predictive maintenance, leading to smarter construction solutions.
Impact of Technology on Structural Steel Construction
Technology continues to reshape how structural steel is utilized in construction. From Building Information Modeling (BIM) to virtual reality for design visualization, these tools provide enhanced collaboration among stakeholders, leading to better outcomes and fewer discrepancies during construction. Additionally, the incorporation of IoT (Internet of Things) devices into structural systems allows for real-time monitoring of structural integrity and safety.